链接
Codeforces Round #496 (Div. 3) - E2. Median on Segments (General Case Edition)
0x00问题转化
为求得中位数为m的所有区间组合,可以将问题转化为两个更容易的问题
“求<中位数为大于等于m的数>的所有组合数量 - <中位数为大于等于m+1的数>的所有组合数量”
0x00求解问题
求<中位数为大于等于m的数>的所有组合数量
从左到右遍历输入数据,若遇到大于等于m的则+1,否则-1 若某个区间[a,b]中+1 -1的和最终大于0(即大于等于m的数多于小于等于m的数),则[a,b]区间的中位数大于等于m
统计这些区间的数目,就是答案 但是遍历区间复杂度是n^2,要计算每一个子区间的和值,可以采用类似于前缀数组的思想, 但是这样整体的复杂度至少是n^2,数据量n最多是20w,可能会出现TL,
参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/widsom/p/9290269.html
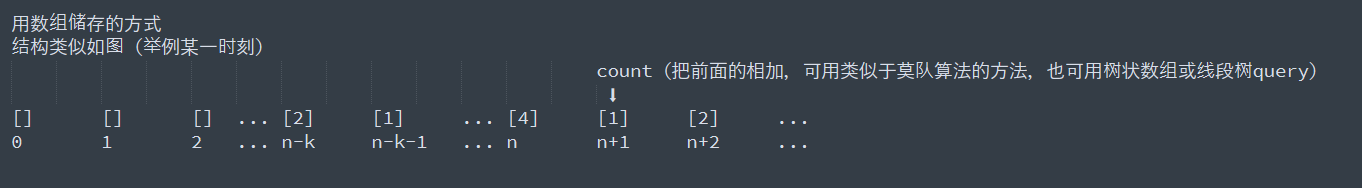
优化: 要统计[a,b]大于0出现的次数,也就是统计“[0,b]的值 > [0,a-1]的值”这种情况出现的次数, 可以采用一次遍历输入数据,假设访问到第c个数,0,k可采用类似于前缀数组的方式迭代计算,
同时用数组或map来保存先前[0,k] (k=0,1,2…c-1)的值出现的次数, 将小于[0,c]的值出现的次数相加,所有的c都这样操作,加起来的就是答案 为将小于[0,c]的值出现的次数相加,可以采用类似于莫队算法的办法,边界一次移动一格
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 200005
int an[MAXN];
int appear[MAXN * 2];//数组开两倍,从中间开始用以满足加减
int n;
long long solve(int m) {
int count = n;// 使用数组从中间开始
appear[count]++;
long long mo = 0;
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (an[i] >= m) {// +1
mo += appear[count];
count++;
appear[count]++;
} else {// -1
count--;
mo -= appear[count];
appear[count]++;
}
ans += mo;
}
return ans;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
int m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", an + i);
}
long long ans = solve(m);
memset(appear, 0, sizeof(appear));
ans -= solve(m + 1);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}